Michael Reitmaier, Ulrich Kulozik, and Petra Först
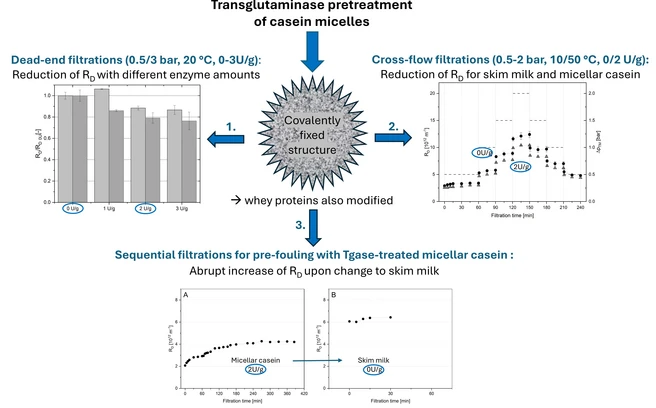
The covalent cross-linking of caseins by the enzyme transglutaminase (Tgase) stabilizes the structure of casein micelles. In our study, the effects of a pretreatment of skim milk (SM) by Tgase on milk protein fractionation by microfiltration were tested. Tgase was found to induce amount-dependent modifications of all milk proteins in SM and a reduction in deposit resistance for laboratory dead-end filtrations of up to 20%. This improvement in process performance could partially be confirmed in pilot-scale cross-flow filtrations of Tgase-pretreated SM and micellar casein solutions (MCC). These comparative trials with untreated retentates under a variation of ΔpTM (0.5–2 bar) at 10 and 50◦ revealed distinct differences in deposit behavior and achieved the reduction in deposit resistance in a range of 0–20%. The possibility of pre-fouling with enzymatically pretreated MCC prior to SM filtration was also investigated. Under different pre-fouling conditions, practical modes of retentate change, and pre-foulant compositions, a switch to untreated SM consistently resulted in an immediate and major increase in deposit resistance by 50–150%. This was partially related to the change in the ionic environment and the protein fraction. Nevertheless, our results underline the potential of Tgase pretreatment and pre-fouling approaches to alter filtration performance for different applications.