Increasing the material utilisation potential of lignin from the pulp industry as protein-based stabilising agent for the beverage
| This project is aimed at finding new material uses for lignin(s) in the beverage industry. For this purpose, various lignin types, namely Kraft lignin, lignosulfonate and biorefinery lignin (e.g., generated in large quantities as by-products in the pulp and paper production and so far, mainly energetically utilised) shall be used as innovative, protein-based stabilising agents in the beverage industry (wine, pome and stone fruit juice, beer) to reduce turbidity. Here, lignin is used as stabilising agent for the depth and surface filtration on a laboratory as well as pilot scale (industrial partner). Analytical core tasks of this research project carried out at Holzforschung München include the chemical as well as structural analysis of the lignin(s), for example by means of evolved gas analysis and pyrolysis-GC-MS, the solubility by means of an FT-NIR rapid measurement method to be developed in the project, and the deposition of secondary substances (sulphur, sodium, magnesium) via AAS, EDXA, ICP-OES or ICP-MS and HPLC. | |
| The technological core tasks carried out by the research partner include the enzymatic cross-linking and purification of the lignin-containing starting samples with the aim of complete insolubility. Lignin is used as protein-based stabilising agent similar to silica gel, bentonite, etc. Finally, an analytical and sensory validation of the consistent product quality is carried out. | |
| The cooperation of both research centres should enable to establish the renewable raw material lignin as a stabilising agent with the aim of increasing resource efficiency and conservation (upcycling) and thus create the basis for its use as technical additive in the beverage industry. Moreover, the pulp industry gains an alternative sales market for the economic and sustainable use (bio-economic) of lignin. | |
| Duration | 01.10.2021 - 30.09.2023 |
| Project Manager | Wanschura, Regina; Windeisen-Holzhauser, Elisabeth; Özparpucu, Merve; Richter, Klaus |
| Project coordination and partner | TUM, Lehrstuhl für Brau- und Getränketechnologie; Kerpes, Roland; Becker, Thomas |
| Funding |

|
| Participating research associations |
Wissenschaftsförderung der Deutschen Brauwirtschaft e.V. – Wifö 
|
Internationaler Verein für Technische Holzfragen e.V. – iVTH 
|
Joint project: vacuum insulation panels based on wood fiber; Subproject 2: Raw material optimization and modification, chemical analysis, ecological and economic assessment - acronym: WoodVIP

| The research project 'WoodVIP' is intended as a feasibility study to examine the potential of vacuum insulation panels based on wood fiber and thus contribute to the use of wood-based materials in new market areas and to increasing the added value of wood products. | |
| The research project examines the suitability of wood fiber-based materials as core material for vacuum insulation panels (VIP) in technical (e.g. transport boxes) and building applications (e.g. insulation of the building envelope). The ‘WoodVIP’ produced in this way should have a comparable thermal conductivity in the range of 0.007 - 0.009 W / (m K) compared to conventional VIPs with cores of fumed silica. | |
| Moreover, the use of a renewable raw material as core material is expected to have significant advantages in terms of sustainability of the WoodVIP, as the environmental impact of VIPs is largely influenced by the core material. The use of comparatively inexpensive wood fibers as core material also enables cost advantages in the manufacture of the WoodVIP. Compared to conventional, air-filled wood fiber insulation materials, there are advantages due to the fact that WoodVIP's thermal conductivity is 5 - 7 times lower. This enables thinner constructions and the potential for substitution of wood fibers compared to conventional insulation materials is increased through the more efficient use of materials. In addition, the impacts of moisture on the thermal conductivity as well as of wood-destroying fungi or molds are avoided by the high barrier films, without the need for any additives. In the project, the influence of different wood species and fiber dimensions on the thermal conductivity, durability, life cycle assessment and economic aspects of WoodVIP is examined and evaluated in comparison to conventional wood fiber insulation materials and conventional VIPs for representative applications. | |
| Scientific and technical work goals: | |
| — Reduction of the thermal conductivity and thus the material use of the WoodVIP compared to conventional wood fiber-based insulation materials | |
| — Increase in the substitution potential of conventional insulation materials | |
| — Improvement in the durability of WoodVIP compared to conventional wood-fiber-based insulation materials, without using additives. | |
| — Significant reduction in the costs of WoodVIP compared to VIP based on fumed silica with comparable thermal conductivity. | |
| — Improved ecological balance and easier recycling of WoodVIP compared to classic vacuum panels thanks to the use of renewable raw materials as the core material. | |
| — Opportunities for recycling wood fibers from hardwood in a product segment with high margins (high-performance insulation materials). | |
| — Expansion of the product range of insulation materials made from renewable raw materials for the production of space-saving components in the area and for the highly efficient over-insulation of connections in cramped situations. | |
| — Investigation of the use of WoodVIP for use in transport boxes. | |
| In the sub-project at Holzforschung München, the outgassing behavior of wood fibers due to volatile substances is investigated and modification processes for pressure stabilization are tested. The data on the resulting manufacturing process and the raw materials required for this are introduced into a life cycle assessment study as well as an economic feasibility study for the sustainability assessment of the developed panels. |
| Duration | 01.12.2021 – 30.11.2023 |
| People | Chair of Wood Science: Engelhardt, Max;; Windeisen-Holzhauser, Elisabeth; Sander-Titgemeyer, Anna; Weber-Blaschke, Gabriele; Richter, Klaus |
| Project partners | Forschungsinstitut für Wärmeschutz e. V. München: Project coordination and execution of sub-project 1 (manufacturing, product properties, building physics investigations and durability) |
| STEICO SE Feldkirchen: Participation in project meetings, consulting, production and tests, provision of industrially manufactured fiber material, production of a demonstrator (wall / roof component using woodVIP) | |
| Va-Q-tec Würzburg: Participation in project meetings, consulting, provision of test material, production of vacuum insulation panels with a wood fiber core as a demonstrator, production of cool boxes with a wood fiber core as a demonstrator, qualification tests on demonstrators | |
| Project Management Agency | Agency for Renewable Resources |
| “Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V. (FNR)” | |

|
|
| Funding granted by: |

|
Development of future-proof concepts for agricultural buildings with wood - from planning to deconstruction (ZukunftLaWiBau) Sub-project: wood products, resource potential and value chains

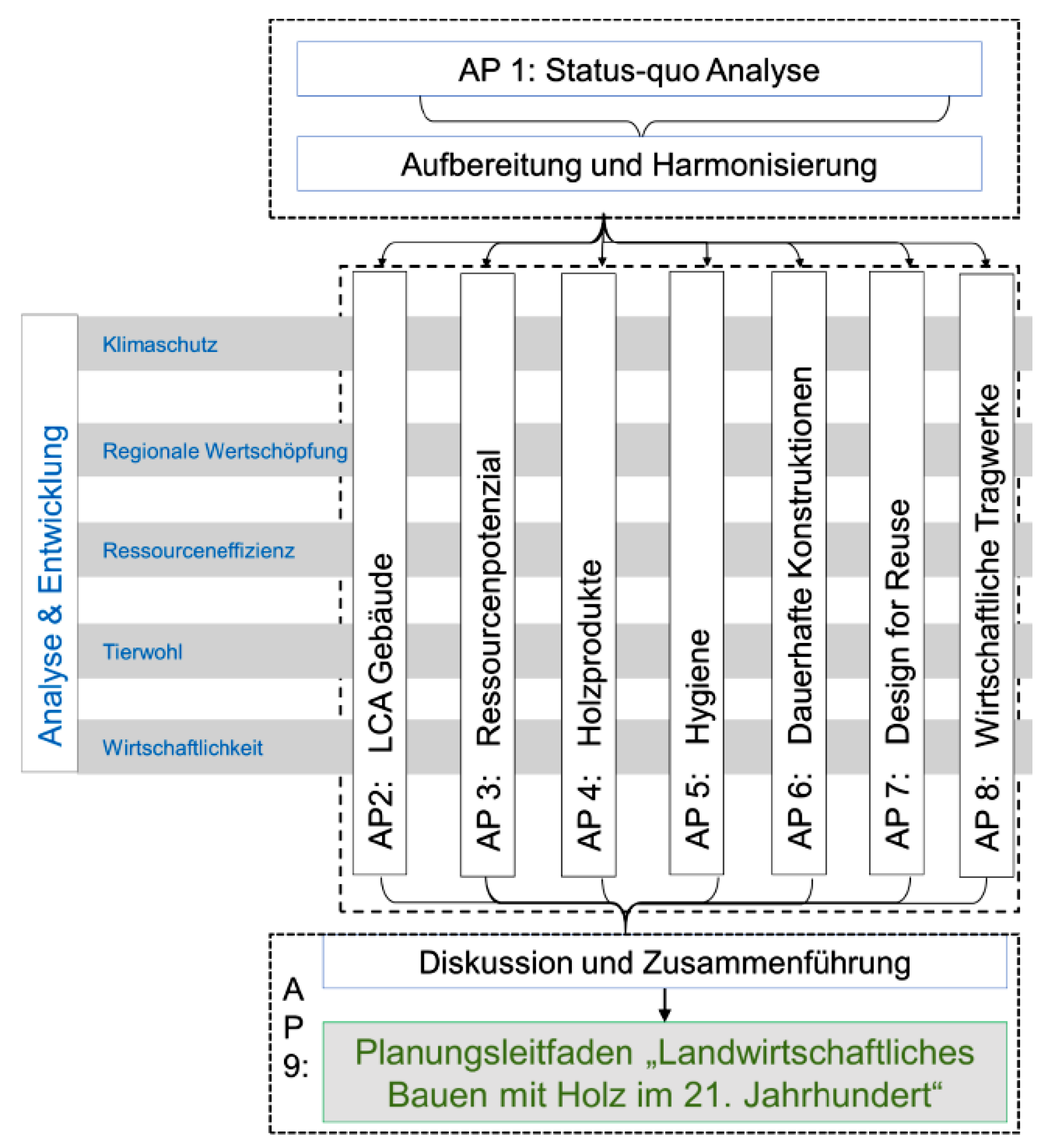
| The objective of the project is to increase the share of agricultural buildings with wood, considering current technical challenges. Towards this aim, planning principles for agricultural buildings will be transferred into the 21st century on the basis of prototype buildings. This involves the integration of regional value chains in rural areas, the consideration of current issues of hygiene and wood products and the development of possibilities for using the potential of existing construction wood. In addition, the database on climate and resource protection of agricultural buildings made with wood will be updated and deepened, and rendered usable for the Charta-for-Wood 2.0 Process. The result of the project is a planning guideline "Agricultural Building with Wood in the 21st Century". The guideline includes current issues - climate protection, animal welfare, regional value creation, durability, resource efficiency and economic efficiency as cross-sectional fields. These issues will be tackled holistically by an interdisciplinary research team. | |
|
|
| Duration | 2020 - 2023 |
| People | AP3 and AP4: Chair of Wood Science: Wanschura, Regina; Helm, Sabine; Windeisen-Holzhauser, Elisabeth; Richter, Klaus; Weber-Blaschke, G. |
| With AP3 "Resource Potential", the project part of Wood Research Munich focuses on a fundamental characterization of farms, which means the analysis of their needs and possibilities concerning wood construction. The resource potential of the farm woodlands will be approximately quantified nationwide. In selected regions, actors in the previously used value chain as well as the material flows are identified and qualitatively and quantitatively investigated. Additionally, interviews are conducted regarding the success factors and obstacles. The potential of buildings with own or regional wood will be presented and recommendations for optimising regional value chains will be highlighted. With AP4 "Wood Products", the focus is on the experimental investigation of different types of wood and (innovative) wood products in terms of their properties, which are necessary for the special conditions of agricultural construction. This is done by laboratory experiments and field tests. The aim is to catalogue the advantages and disadvantages of each type of wood and each type of wood material in defined scopes based on selected criteria (chemical/physical/technical properties) for agricultural construction. | |
| project partners | Ruhr-Universität Bochum (Chair for Resource Efficient Building, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Annette Hafner) Coordination and AP2 "LCA Buildings": Creation and validation of the LCA of agricultural buildings of various construction methods (e.g. complete timber construction and partial timber construction) as well as the elaboration and presentation of associated ecological characteristics |
| Bavarian State Research Center for Agriculture (LfL), Institute for Agricultural Engineering and Animal Husbandry, (Working Group on Agricultural Construction (ILT 4c), Dipl.-Ing. Architect Jochen Simon) AP1: "Status-Quo-Analysis": Inventory analysis and data determination on the agricultural buildings for animal husbandry and warehousing, selection of model buildings and harmonisation of data, as well as AP8: "Economic structures": development of exemplary structural variants from the aspect of economic efficiency | |
| Freie Universität Berlin (FUB), Department of Veterinary Medicine, Institute for Animal and Environmental Hygiene (Prof. Uwe Rösler) | |
| Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI), Federal Research Institute for Animal Health (Prof. Dr. Franz J. Conraths) AP5 „Hygiene“: Examination of the properties of wood building materials regarding hygiene requirements in agricultural production, comparison of wood with other building materials (steel, plastic, concrete) as well as comparison of the effect of different surface structures of wood products | |
| Technical University of Munich, Department of Civil, Geo and Environmental Engineering, Chair of Timber Structures and Building Construction (Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Winter, Dr.-Ing. Philipp Dietsch, Dipl.-Ing. MA Architekt Stephan Ott) AP6: "Permanent Constructions": Types of construction and connection types to special stress situations for agricultural construction with wood, as well as AP7 "Design for Reuse": Design for Reuse of agricultural buildings in wood construction (cascade use) | |
| The project is supported content-related by some institutions and interest groups, e.g. by the Bavarian Carpentry Association, by the Cluster Initiative Forest and Wood in Bavaria gGmbH with proHolz Bayern, by the German Timber Management Council (DHWR) and the CCT Council of Timber Technology. | |
| Project Management Agency |
Agency for Renewable Resources (FNR) 
|
| Granted by |
Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture due to a resolution of the German Bundestag - Parliament of the Federal Republic of German
|
| Download | Project flyer |